Take a few minutes to familiarize yourself with the layout of a GitHub repository:
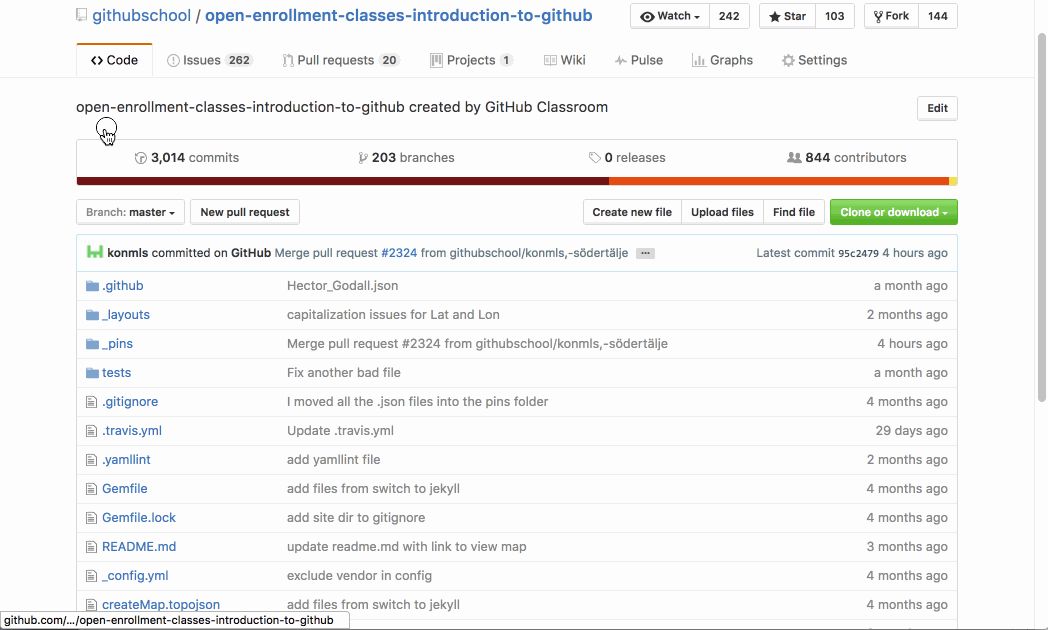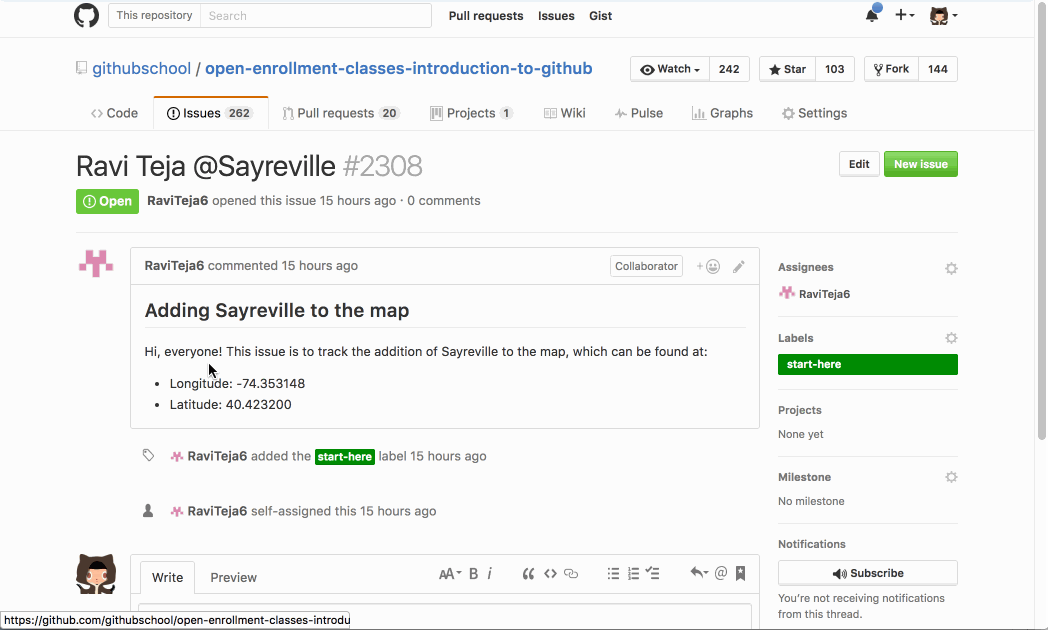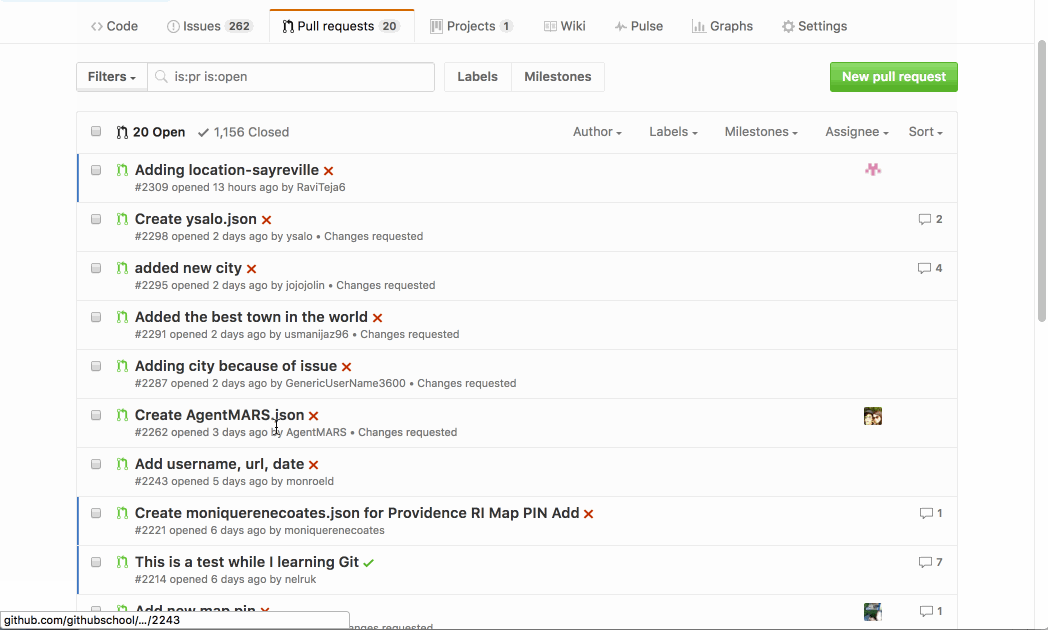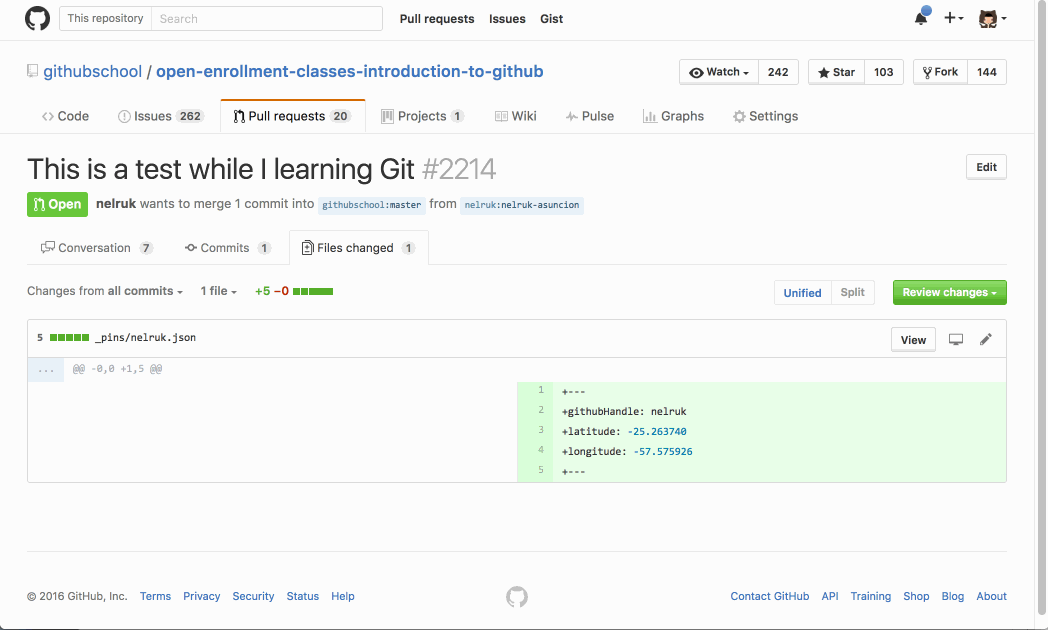
- Watch the video in the Tell me why section for a guided tour.
- Navigate to the Code tab to find the repository README.
- Click on an Issue and a Pull Request to see the difference (HINT: one contains changes to code, the other does not).
- Click Insights and select the Pulse or Graphs sub-options to view some of our repository stats.
Tell me why
Exploring A GitHub Repository
Now that you have a repository, check out this short video to learn about the key features it contains:
More Great Features
The video covered some of the most commonly used features. Here are a few other items of interest you can find in GitHub repositories:
- Projects: You can create Kanban style project tracking boards within GitHub.
- Wiki: GitHub also has a place to create and store your relevant project documentation.
-
Insights: A drop-down menu option that contains links to different analytic tools for your repository. It contains the following items:
- Pulse: Pulse is our project’s dashboard. It contains information on the work that has been completed and the work in progress.
- Graphs: Graphs provide a more granular view of the repository activity, including who has contributed, when the work has been done, and who has forked the repository.
Special Files
In the video you learned about a special file called the README.md. Here are a few other special files you can add to your repositories:
-
CONTRIBUTING.md: The
CONTRIBUTING.mdis used to describe the process for collaborating on the repository. The link to theCONTRIBUTING.mdfile is shown anytime someone begins to create a new issue or pull request. -
ISSUE_TEMPLATE.md: The
ISSUE_TEMPLATE.mdis yet another special file you can use to pre-populate the body of an issue. For example, if you always want to gather certain types of information for bug reports, you can include it in the issue template and every new issue will be opened with your recommended starter text.
Stuck? Open an issue in the repository for this class and mention @githubteacher for help from one of the GitHub trainers!